Quite often, we see clogged nipples (completely or partially) when water medication is not administered correctly or if the requirements for successful water medication are not met.
Clogged nipples can cause reduced water intake and lower ADG as well as drinking water medication treatment failure due to underdosing.
It is important to understand what exactly is causing the blocking of the nipples, so you can prevent this in the future. The most common causes of clogged nipples are:
Biofilm Formation
Biofilm is a slime (very much like tooth plaque) produced by bacteria in the water. It not only clogs nipples, but the micro-organisms in the biofilm can produce enzymes that degrade certain antimicrobials, which impede treatment. It may also contain resistant bacteria that can cause animal disease.
This usually begins with scaling or iron and/or manganese particles attaching to the pipe wall.
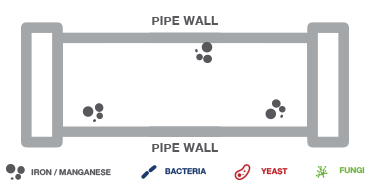
This allows bacteria in the water to attach to these deposits.
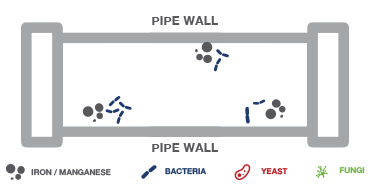
The bacteria replicate and form a glycocalyx, a layer of growth medium and more bacteria (like tooth plaque), and the formation of the biofilm begins.
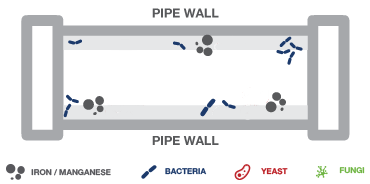
If the water contains fungi and yeast, these will also start to replicate.
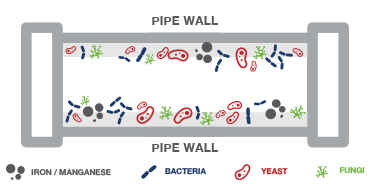
There are several risk factors affecting biofilm formation. The most important ones are:
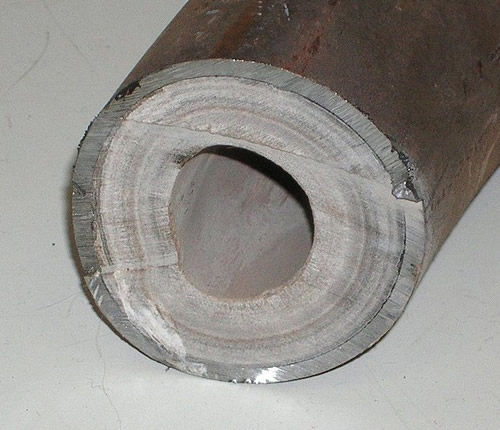
Scaling
Deposits resulting from high calcium and/or magnesium levels are called scaling. They will not only reduce water flow, but also create a rougher inner surface of the pipes, which makes it easier for bacteria to latch on and form colonies that may lead to biofilms.

Interactions with other products
Combining different products that are perfectly soluble on their own can sometimes create a problem of precipitation. This can happen with two pharmaceutical products, but also when combining, for example, an antimicrobial with a product for cleaning and disinfection at low dosage (like sodium hypochlorite or hydrogen peroxide).
Please be aware that not all interactions are visible. Sometimes an active substance is completely neutralised by another substance while the solution is still perfectly clear.
In general, combination of products is off label and not advised.
Manganese
If the manganese concentration is > 2 mg/L, there are two possible reactions:
